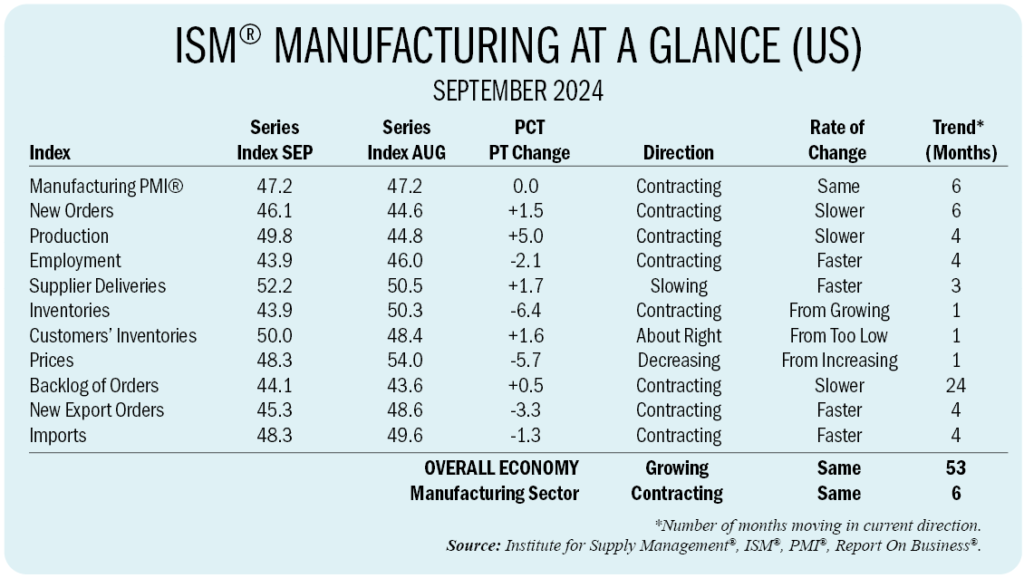
US Manufacturing PMI Holds at 47.2 Percent in September
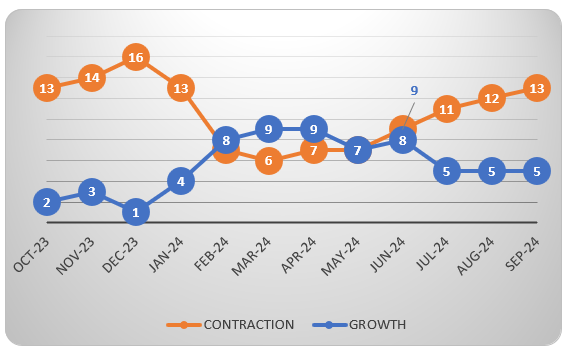
Global Manufacturing Slows Overall But Canada Pushes Into Growth Mode
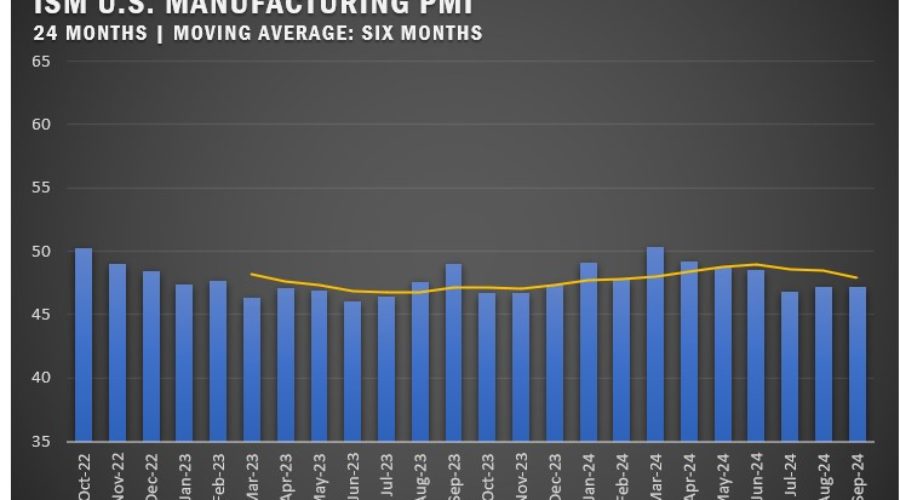
The ISM U.S. Manufacturing PMI held steady at 47.2 percent in September, matching August’s figure and marking the sixth consecutive month of contraction. According to Timothy R. Fiore, Chair of the ISM Manufacturing Business Survey Committee, demand continued to weaken while production showed signs of stabilizing.
The New Orders Index rose slightly to 46.1 percent but remained in contraction territory, while the Production Index approached expansion, registering 49.8 percent, a significant five-point jump from August. The Employment Index dropped to 43.9 percent as manufacturers continued right-sizing their workforces. Prices fell into contraction for the first time this year, with the Prices Index at 48.3 percent.
Supplier deliveries slowed, with the Supplier Deliveries Index at 52.2 percent, indicating some supplier challenges. Inventories contracted sharply, as the Inventories Index dropped to 43.9 percent, and new export orders shrank at a faster pace, falling to 45.3 percent.
Manufacturing activity remains sluggish, with 77 percent of manufacturing GDP contracting in September. Despite stabilizing production, subdued demand and political uncertainty are holding back the sector. Of the six largest manufacturing sectors, only the Food, Beverage and Tobacco Products segment showed growth in September, compared to two in in the prior month.
COMMODITIES
Up in Price: Aluminum* (10); Corrugate (3); Corrugated Boxes (3); Electrical Components (5); Ocean Freight (5); Plastic Resins (9); Polypropylene Resin (3); Steel Products*; and Synthetic Fibers. Down in Price: Aluminum* (2); Copper (3); Crude Oil; Diesel Fuel; Steel (5); Steel — Stainless; and Steel Products* (4). In Short Supply: Electrical Components (48); and Electronic Components (6). *Indicates both up and down in price.
US SECTOR REPORT
ISM GROWTH SECTORS (5): Petroleum and Coal Products; Food, Beverage and Tobacco Products; Textile Mills; Furniture and Related Products; and Miscellaneous Manufacturing.
ISM CONTRACTION SECTORS (13): Printing and Related Support Activities; Plastics and Rubber Products; Wood Products; Apparel, Leather and Allied Products; Primary Metals; Transportation Equipment; Nonmetallic Mineral Products; Electrical Equipment, Appliances and Components; Paper Products; Machinery; Chemical Products; Fabricated Metal Products; and Computer and Electronic Products.
SEPTEMBER ISM REPORT COMMENTS
(U.S. Manufacturers)
“North American demand has started to weaken. Asian demand is slightly higher but shows signs of weakness in future months. Comments tied to automotive builds.” Chemical Products
“Global demand continues to remain soft. Fourth-quarter forecasts have been further reduced, with several new programs shifted from 2024 to 2025. Manpower, working capital and supplies are being flexed down in response. The previously anticipated shift from internal combustion engine to electric vehicle (EV) technology has been pushed out due to market response. Long-range plans are being adjusted to incorporate traditional products for longer, while new EV product offerings are being planned for slower rollouts.” Transportation Equipment
“The second half of 2024 is trending upward enough to more than compensate for the year-over-year losses we experienced in the first half. We are anticipating a record sales volume for 2024.” Food, Beverage and Tobacco Products
“The strategy of customer push-outs last year enabled those customers to adapt to the market. Now, while most companies are seeing a slowdown, we are seeing solid growth. The general slowdown in the economy is allowing for prices to continue to stabilize.” Computer and Electronic Products
“A continuing low order rate is resulting in ongoing manufacturing adjustments to balance output with demand.” Machinery
“The fourth quarter is slower than anticipated. We won’t realize the effect of interest rate adjustments with new project starts until the first quarter of 2025.” Fabricated Metal Products
“Business is flat. Waiting for interest rates to drop and the election outcome in November before we confirm our 2025 plans. Currently planning on a flat 2025.” Furniture and Related Products
“Our sales continue to be flat. Our customers are telling us that although our products perform very well, they are forced to seek lower-cost components to maintain their sales.” Textile Mills
“Sales have slowed this quarter compared to the same time period last year. Adjusting production accordingly.” Miscellaneous Manufacturing
“Still hiring to fill vacant positions in production/management. Not adding new jobs. Automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are starting to slow or cancel orders. The pace is slowing.” Primary Metals
GLOBAL PMI NOTES
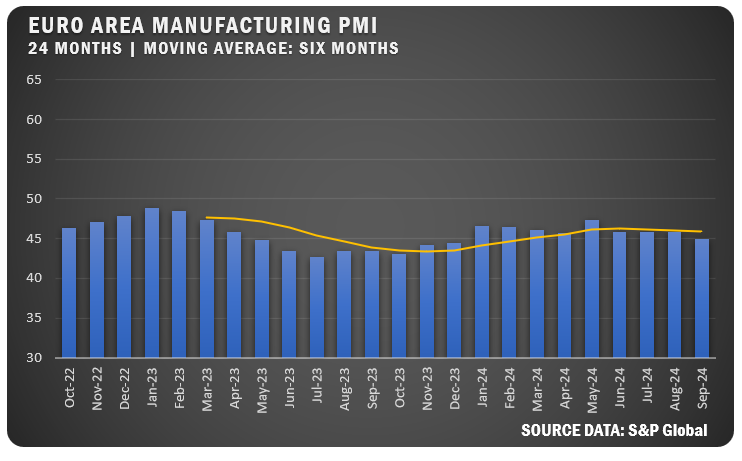
EUROZONE: The HCOB Eurozone Manufacturing PMI registered 45.0 percent in September, falling from a 45.8 percent reading in the previous three months. The new figure is the lowest reading of the year as the sector deepens into contraction. Production and new orders fell sharply, with job losses reaching their highest level since October 2012. Input costs declined for the first time since May.
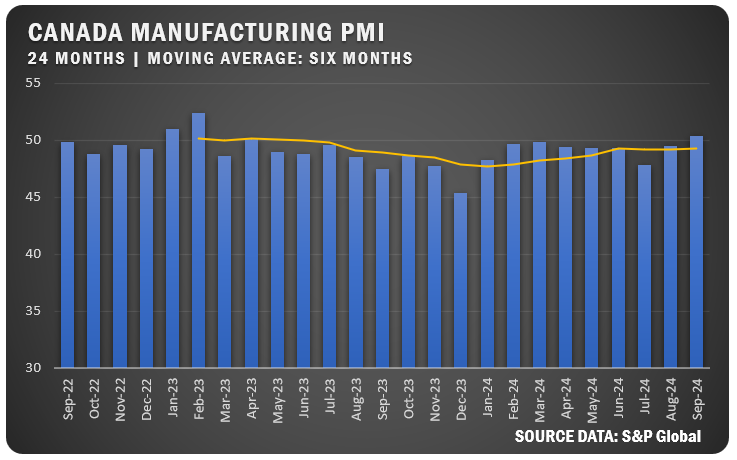
CANADA: Canada’s S&P Global Manufacturing PMI rose to 50.4 percent in September, signaling the first improvement in operating conditions since April 2023. A slight rise in new orders, driven by domestic demand helped push up the number. The country’s manufacturers saw marginal employment gains, but export orders continued to decline and input costs accelerated to a 17-month high.
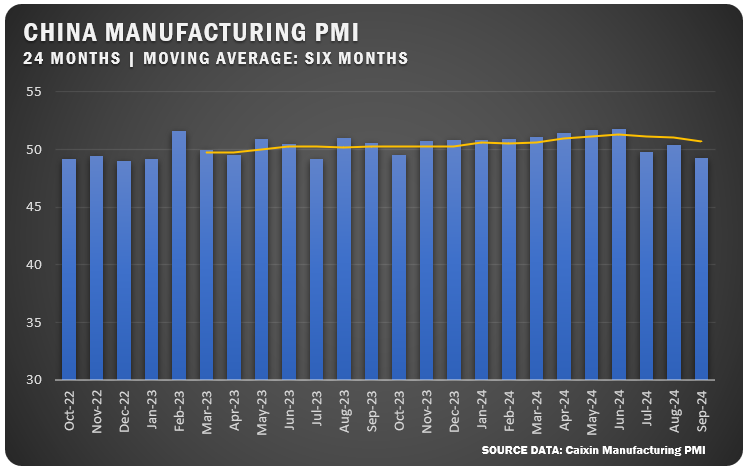
CHINA: The Caixin China Manufacturing PMI dropped to 49.3 percent in September 2024, marking the lowest level since July 2023. The fall into contraction territory occurred as new orders fell to a two-year low and export orders also declined. Input costs and output prices decreased sharply due to heightened competition and weaker demand.
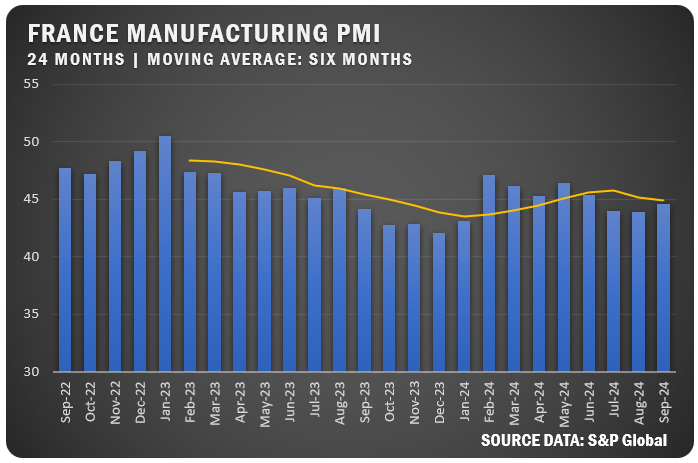
FRANCE: France’s S&P Global Manufacturing PMI improved slightly to 44.6 percent in September, though it remained in contraction for the 20th consecutive month. Output and new orders continued to fall sharply, while input price pressures eased. Accordingly, business confidence hit its lowest level since January as firms expressed concerns about ongoing political uncertainty.
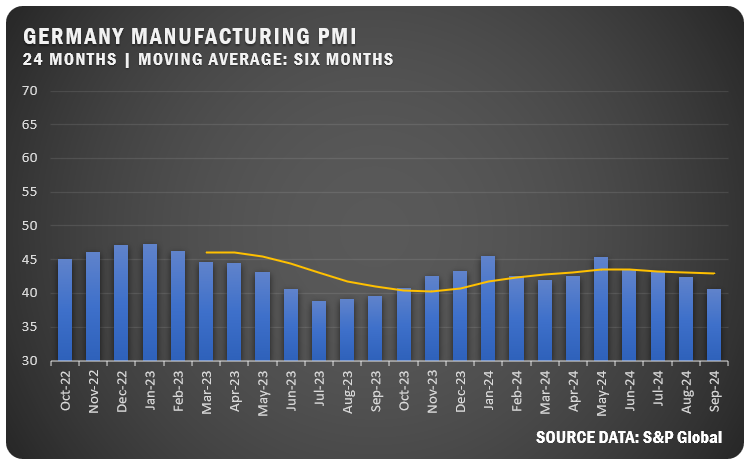
GERMANY: Germany’s HCOB Manufacturing PMI dropped to 40.6 percent in September, the lowest in a year, highlighting a deepening contraction in the sector. New orders fell sharply, particularly in the auto sector and employment levels sank at the fastest rate in four years as weak demand continued to pressure output and purchasing activity.
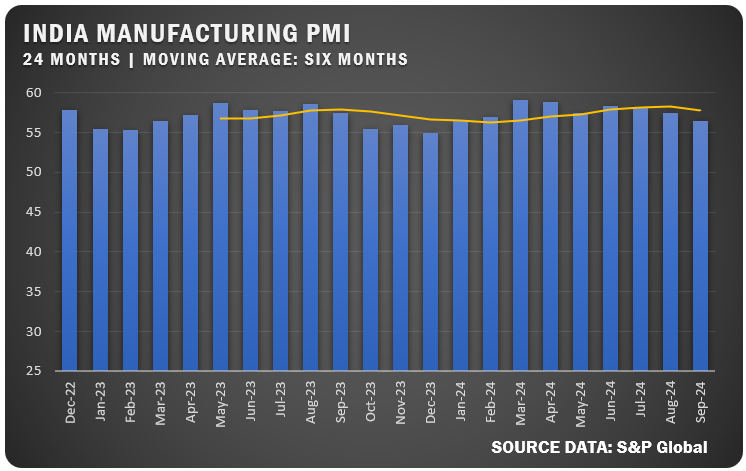
INDIA: India’s HSBC Manufacturing PMI fell to 56.5 percent in September, marking the softest expansion since January. New orders and output grew at a slower pace, while export orders dropped and business confidence reached its lowest level since April 2023.
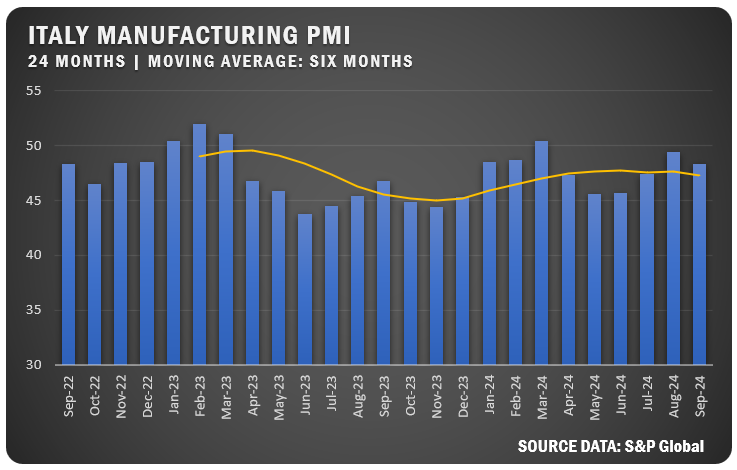
ITALY: Italy’s HCOB Manufacturing PMI fell to 48.3 percent in September as weak demand drove sharper declines in new orders and output. Despite the downturn, hiring expanded for the second consecutive month, while business sentiment fell below the historical average due to a pessimistic outlook for future output.
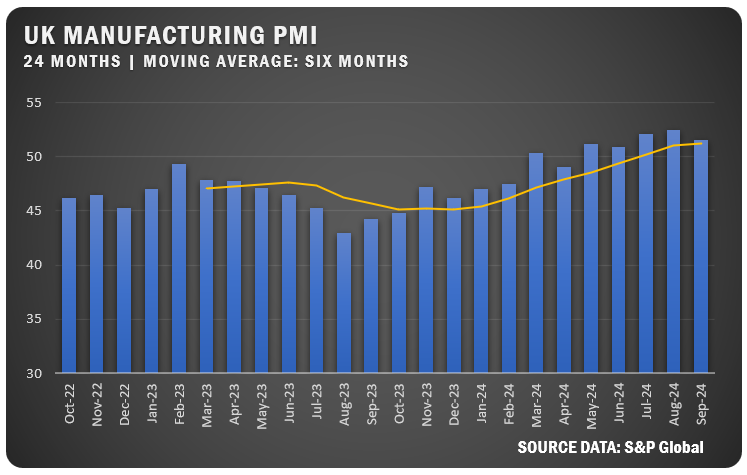
UNITED KINGDOM: The UK S&P Global Manufacturing PMI dropped to 51.5 percent in September, indicating expansion but with slower growth in output and new orders. Strong domestic demand supported the sector, but rising input costs and export weakness led to reduced employment and purchasing activity. Businesses were still optimistic about the future outlook, but not quite at the same level as seen in the previous month.
Source: Institute for Supply Management®, PMI® (Purchasing Manager Index), Report On Business®. For more information, visit the ISM® website at www.ismworld.org.